Perovskite-perovskite-silicon triple-junction solar cells have technical potential to reach 44.3% efficiency
optical properties of perovskite/perovskite/silicon triple-junction cells suggest 44.3%
roadmap includes the adaption of the perovskite absorber thicknesses, modifying bandgaps, employing a fully textured cell, and optimizing the thicknesses of the interlayers between the absorbers
researchers initially assumed the triple junction cell to be based on a bottom silicon heterojunction cell with an indium tin oxide (ITO) layer and a silver (Ag) metal contact, a middle perovskite cell with an energy bandgap of 1.57 eV, and a top perovskite cell with a bandgap of 1.84 eV
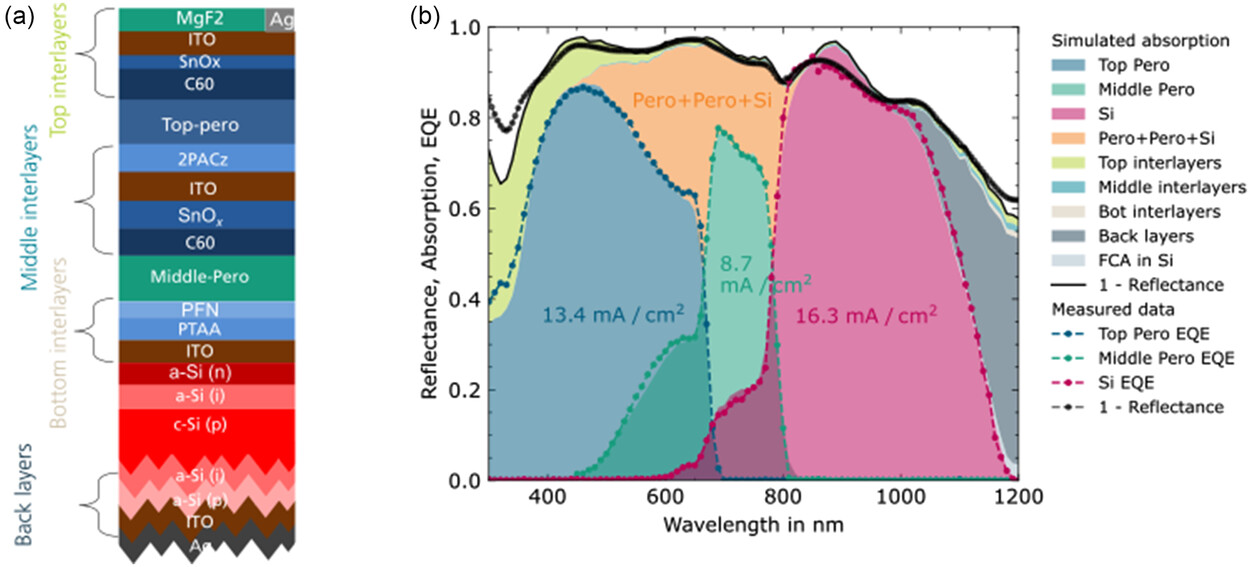
In the optimization process, their efforts were directed to increase the photocurrent of all three cells
varied the thicknesses of the three absorbers and then they adjusted the perovskites bandgaps. Moreover, they applied a textured front side to mitigate reflection losses and used thinner interlayers
simulation showed that the best cell configuration may potentially achieve a power conversion efficiency of 44.3%, an open-circuit voltage of 3480 mV, a short-circuit density of 14.1 mA cm−2, and a fill factor of 90.1%